AP19174909 Improving the quality of contact butt welding of reinforcing rods and heterogeneous cylindrical workpieces by optimizing modes
Relevance: Development of the Technological Capabilities of the Butt Welding Method for Joints
Results Achieved in the 2nd Half of 2025:
1) Тhe technological capability of the joint welding method has been improved by optimizing modes using computers and computer simulations.
2) Рlanning an experiment. In order to improve the quality of the contact joint welded joint, experiments were carried out, mathematical dependencies were identified, and a regression equation was obtained.
3) Тo determine the strength of the welded joint, a static tensile test was carried out on the samples and the tensile strength limit was determined depending on the loads.
4) Мodeling was carried out in SolidWorks in order to compare the results obtained from tensile tests.
List of Publications for the 2nd Half of 2025:
Foreign publications:
1. Aiym Yessirkepova, Karibek Sherov, Medgat Мussayev, Nazerke Abisheva, Nursulu Tuliyeva. Investigation of the quality of joining cylindrical blanks by resistance flash-butt welding // International Journal of Innovative Research and Scientific Studies, 8(6) 2025, pages: 3067-3078. In the Scopus CiteScore 2.1 database, the percentile is 67%. Q2.
https://ijirss.com/index.php/ijirss/article/view/10269
2. Yessirkepova, A., Sherov, K.T., Absadykov, B.N., & Sikimbaev, M.R. Joining of metallic cylindrical workpieces by contact butt welding and tensile testing. (А. Есиркепова, К.Т. Шеров, Б.Н. Абсадыков, М.Р. Сихимбаев. Соединение металлических цилиндрических заготовок способом контактной стыковой сварки и испытание на растяжение), december 2025y, the percentile is 72%. Q2.
Domestic publications:
1. Yesirkepova A.B., Sherov K.T. Experimental Study of Methods for Butt Joining Reinforcing Bars. Proceedings of the International Scientific and Practical Conference “Development of the Machine-Building Industry and Training of Highly Qualified Specialists of a New Generation,” dedicated to the 60th anniversary of Doctor of Technical Sciences, Professor Karibek Tagaevich Sherov of the S. Seifullin Kazakh Agrotechnical Research University. – Astana: KazATU Publishing House, 2025. – pp. 198–200.
https://kazatu.edu.kz/ru/pages/nauka/novosti-nauki_20220121052309/sborniki-naucnyh-konferencij
2. A.B. Yesirkepova, N.B. Abisheva, A.K. Sherov, N.Zh. Karsakova, S.I. Mendaliyeva. Quality Control of Butt-Welded Joints Using the Mirror-Shadow Method. Science and Technology of Kazakhstan, No. 3 (2025), pp. 64–78.
3. Monografıa. A.B. Yessırkepova, K.T. Sherov. Technology of joint welding of reinforcing rods and heterogeneous cylindrical workpieces: monograph /Yessirkepova A. B., Sherov K. T.; Nao “Karaganda Technical University named after Abylkas Saginov”. – Karaganda: Publishing House of NAO “Abylkas Saginov Karaganda Technical University”, 2025, -106 P. ISBN 978-601-355-596-6.
Research Group:
1. Scientific Supervisor: PhD, Senior Lecturer Yessirkepova Aiym Bakytbekovna
2. Scientific Consultant: D.Sc., Professor Sherov Karibek Tagaevich
Information for Potential Users:
A metallographic study (inspection) was carried out on welded joints obtained by butt welding (fusion) of the base metal and various materials. From different samples produced by butt welding under various regimes, polished sections (shlifs) were prepared.
 а) а) |
 б) б) |
 в) в) |
a) Hardware grinding process; b) Stepwise grinding to a mirror finish; c) Prepared samples
Figure 1 – Process of preparing a polished section from various samples
After preparing the polished section, the microstructure of the samples was examined using a MAGUS optical microscope, and in some samples, defects were identified: white spots, metal burn marks, presence of oxides, blockage by non-metallic inclusions, microscopic cracks, bubbles, and other structural defects.
а) |

б) |

в) |

г) |
a) White spots, b) Pores, c) Microcracks, non-metallic inclusions d) Defect-free
Figure 3 – Microscopic analysis of various welded samples
As a result of the macro- and microstructural analysis of the polished sections, it was found that in 95% of the samples, in the welded seam (samples produced under optimal welding conditions), no cracks, melts, or unbonded defects, holes, bubbles, slag, or other inclusions were detected.
The results obtained were tested and transferred to “design bureau STEP” LLP for implementation of the research results in production.
Scope of application of the results: In Mechanical Engineering and construction industry.
AP19175058 Numerical modeling of cutting processes of hard-to-machine materials in the conditions of mechanical engineering enterprises of the Republic of Kazakhstan
Relevance
Despite advances in technology for reshaping parts, machining remains the primary method of production. High demands on surface quality necessitate the improvement of machining technologies for large-scale parts. Machine-building enterprises in the Republic of Kazakhstan (RK) face particular challenges when manufacturing grooves, steps, flutes, and edge recesses from difficult-to-machine materials. Conducting full-scale experiments to determine optimal cutting conditions that ensure the required surface quality is expensive and ineffective. The efficiency of machining difficult-to-machine materials can be improved through numerical modeling of machining processes in universal software packages. This, in turn, requires the development of a new machining modeling methodology. This methodology allows for obtaining data on deformations, stresses, temperatures, and the distribution of cutting forces within the machining zone. Analysis of the obtained results enables the selection of optimal cutting parameters and tool geometry, as well as increasing tool life and surface finish quality.
Results achieved in the second half of 2025:
This paper develops a numerical simulation methodology for high-speed milling of 15Kh12VMF high-alloy steel. A model of the tool-workpiece system, taking into account its physical and mechanical properties, was constructed using the Johnson-Cook model in ANSYS Workbench. The influence of cutting conditions on temperature and stress was determined, and the feasibility of predicting thermal deformation fields and tool wear in the milling zone was demonstrated. The obtained results provide a scientific basis for optimizing milling conditions for difficult-to-machine materials.
List of publications for the 2nd half of 2025.
In 2025, based on the results of the research, the following works were published in foreign publications:
1. Donenbayev B, Sherov K, Mardonov B, Makhmudov L, Magavin S, Rakishev A and Sherov A (2025) Research and modeling of the high-speed milling process of heat-resistant high-alloy steel. Front. Mech. Eng. 11:1680007.https://doi.org/10.3389/fmech.2025.1680007;
2. Donenbayev, B., Sherov, K., Bakirov, M., Tazhenova, G., & Rakishev, A. (2025). Numerical simulation of milling of difficult-to-machine materials for cutting optimization. International Journal of Innovative Research and Scientific Studies, 8(8), 341–350.https://doi.org/10.53894/ijirss.v8i8.10673. In the Scopus database, CiteScore 2.1., Percentile 67%. Q2.
Research group
Donenbaev B.S. – scientific director, PhD, senior researcher at KazMIRR
Magavin S.Sh. — scientific consultant, candidate of technical sciences, associate professor of KazATIU
Information for potential users
The obtained results laid the scientific basis for improving the design of cutting tools and optimizing the technical and economic indicators of the milling process of difficult-to-machine materials, such as the quality of the machined surface, productivity and energy consumption.
Scope of application
The results of the study and the developed methodology can be used:
– at mechanical processing and tool-making engineering enterprises of the Republic of Kazakhstan;
– when designing technological processes for processing difficult-to-machine materials – heat-resistant, titanium and stainless alloys.
 |
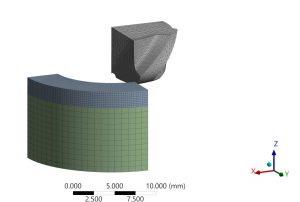 |
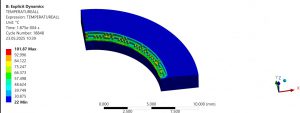 |
AP19174774 «Study on the impact of underground mining on surface social facilities» – s.s. N. Khuangan
Relevance
Ore mining by the room-and-pillar system is one of the most efficient. Significant disadvantages of the technology used are ore losses in pillars left to support the mined-out space (voids), accumulation of voids and their collapse after the destruction of pillars due to a long service life (decades). Sudden collapses of mined-out spaces over large areas are accompanied by man-made earthquakes.
In 1996, after a number of major collapses accompanied by earthquakes, a new concept for further efficient and safe development of the Zhezkazgan deposit in the existing mining and geomechanical conditions was developed, agreed upon with the committee of the state mining and technical supervision of the Republic of Kazakhstan, and approved by the minister of industry and trade of the Republic of Kazakhstan. It set out three fundamental provisions, in accordance with which the industrial exploitation of the deposit would be completed: 1) to develop the remaining balance reserves using the room-and-pillar system, for which, in the conditions of Zhezkazgan, there is no acceptable alternative for mining ore of run-of-mine and lower value; 2) simultaneously with the primary development of the remaining balance reserves, to conduct repeated development of previously abandoned pillars with the return of ore from losses; 3) during repeated development, to extinguish the accumulated voids by controlled self-caving of the overlying stratum.
The main objective of the project is to assess the seismic risk in the area of the village of Zhezkazgan as a result of the impact of mining operations.
The influence of underground mining operations during the development of ore bodies and/or abandoned inter-chamber pillars on the deformation of the earth’s surface with buildings is studied by numerical modeling of the stress-strain state of the massif using finite element methods with the use of the COMSOL and MATLAB application software packages, developed specifically for engineering and scientific research, including in the field of geomechanics.
To assess the impact of underground mining operations on the stability of protected objects, absolute (mm) and relative (mm/m) subsidence of the surface of the displacement trough are used.
Calculations of the rock mass displacement and numerical modeling of the geomechanical state of the undermined sections of the day surface along profile lines will give the values of vertical subsidence. This is a conclusion about possible serious deformations of surface objects falling into the displacement zone, and accordingly – about the need to resettle the residents of the villages of Zhezkazgan and Krestovsky to a safe place.
Achieved Results in the Second Half of 2025
In the second half of 2025, the following results were obtained within the framework of the project:
• a methodology was developed and verified for assessing the impact of underground mining operations on protected surface facilities using numerical modeling of the stress–strain state of the rock mass;
• numerical modeling of the stress–strain state along profile lines was performed, including calculations of vertical subsidence and total displacements of the surface within the subsidence trough;
• quantitative estimates of possible technogenic earthquakes (energy class and magnitude) were obtained based on the established relationship between earthquake magnitude and rock mass displacement; recommendations for applying the MSK-64 scale to assess the risk of building damage were prepared;
• conclusions were formulated regarding the admissibility or inadmissibility of underground mining beneath specific surface facilities and areas of the deposit;
• scientific papers related to the project results were prepared and published, including publications in journals indexed in Scopus and national databases;
• certificates of state registration of intellectual property rights for the developed methods and research results were obtained;
• practical recommendations were developed for potential users (mining enterprises) to optimize the planning of mining operations considering time factor and seismic risk.
List of publications for the 2nd half of 2025
1. Article in the CQAES database. N. Khuangan, S.T. Asainov, R.K. Kamarov, A.Z. Kapasova “Study of the influence of repeated development of reserves on the state of surface objects” DOI 10.52209/1609-1825_2025_1_208. University Works No. 1 (98) • 2025 pp. 208-2015., Section “Geotechnology. Life Safety»
2. Article in the journal Mining of Mineral Deposits (Mining of Mineral Deposits, percentile 76, Q1 (Nurbol Khuangan, Sergey Asainov, Timur Khojayev, Zhanat Azimbayeva, Kobey Atageldiyev, Gulnur Nurshaiykova, Asel Akylbayeva, «Predicting the magnitude of technogenic earthquakes during underground mining of the Zhezkazgan ore field» Mining of Mineral Deposits. ISSN 2415-3443 (Online) | ISSN 2415-3435 (Print) Volume 18 (2024), Issue 1, 45-53. https://doi.org/10.33271/mining18.01.045)
Research group
Khuangan Nurbol, PhD in Mining engineering, associate professor.
Hirsch Index-5,https://www.scopus.com/authid/detail.uri?authorId=57191875943, https://orcid.org/my-orcid
Author ID in Scopus: 57191875943
ORCID ID: 0000-0001-9609-6649
Assainov Sergey Tursunovich, Ph.D., senior lecturer, department of DMDD
Information for potential users
A scientifically based procedure for refining reserves beneath protected surface targets has been developed.
A methodology for assessing the impact of underground mining on surface targets has been developed.
The obtained research results will allow for informed conclusions regarding the feasibility or impossibility of underground mining in specific areas of the deposit.
Scope of application
Mining enterprises engaged in the development of minerals using underground methods.
